Schlieren imaging is an optical technique used to intensify density gradients, and therefore it can be used to track the edge of a flame during flame speed experiments. This overall effect is accomplished by passing a collimated beam of light through the test vessel and then focusing the light into a high-speed camera. The changing radius of the growing flame is then used to determine the stretched, burned-gas flame speed.
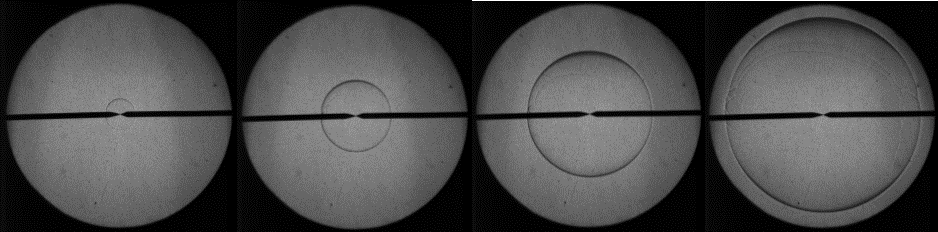
Sample schlieren images of a spherically propagating flame, taken at TAMU in our High Pressure High Temperature Laminar Flame Speed vessel.